|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
|
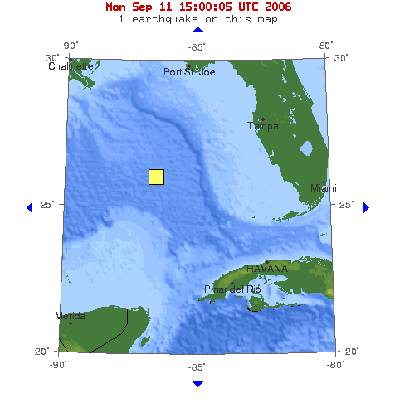
6.0 earthquake in the Gulf of Mexico, September 10, 2006
09.11.06 -- People as far away as New Orleans reported feeling the seismic activity of a 6.0 earthquake in the Gulf of Mexico on Sunday morning, September 10, 2006 at 8:56:07 AM Eastern Time. According to the USGS Earthquake Center, this strong earthquake occurred at a depth of 6.2 miles, 250 miles WSW of Anna Maria, Florida, 260 miles WSW of Clearwater, Florida, and 330 SE of New Orleans, Louisiana. It is quite unusual for this area to experience more than minor or light seismic activity, since this area is not on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
Just to give a little perspective on the size of this quake, I
thought you might want to know how an earthquake is measured.
The hypocentral depth (6.2 miles in this case) is where the
earthquake begins to rupture. The depth may be relative to
mean sea-level or the average elevation of the seismic
stations which provided arrival-time data for Seismologists indicate the size of an earthquake in units of magnitude. There are many different ways that magnitude is measured from seismograms because each method only works over a limited range of magnitudes and with different types of seismometers. Some methods are based on body waves (which travel deep within the structure of the earth), some based on surface waves (which primarily travel along the uppermost layers of the earth), and some based on completely different methodologies. However, all of the methods are designed to agree well over the range of magnitudes where they are reliable. Earthquake magnitude is a logarithmic measure of earthquake size. In simple terms, this means that at the same distance from the earthquake, the shaking will be 10 times as large during a magnitude 6 earthquake as during a magnitude 5 earthquake. The total energy released by the earthquake, however, goes up bey a factor of 32.
Earthquake are classified in the following magnitudes: At the time this article was submitted (September 11, 2006), the latest earthquake in the central US occurred one mile NW of Ridgely, TN on September 7 at 11:07 PM. This was a micro earthquake (magnitude 1.6) at a depth of 4 miles. For more information on earthquakes, visit the USGS website at http://earthquake.usgs.gov or the Center for Earthquake Research and Information (CERI) at the University of Memphis, http://www.ceri.memphis.edu ©2006 Information for this article was compiled by MAGS member, Mike Baldwin. Graphic courtesy of the USGS Earthquake Center. Used by permission. Information used for educational purposes under the provisions of the "Fair Use Act of 1976". Reference: Earthquake Hazards Program; Earthquake Center; US Geological Survey; http://earthquake.usgs.gov; accessed 11 September 2006. Information used for educational purposes under the provisions of the Fair Use Act of 1976.
|
||
|
|
||||