|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
|
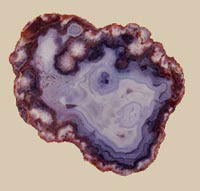
Agates
06.21.00: Agates are a microcrystalline variety of the quartz group of varying colors, a chalcedony. Agates are usually translucent in thin slices, otherwise opaque. Agates occur as spherical or almond shaped inclusions in basic volcanic rock. The stripey appearance is the result of rhythmic crystallization. Under the influence of weathering a white crust forms on the outer layer and in the uppermost agate bands. In the interior of the agate-almonds there are frequently well-developed crystals such as rock crystal, amethyst, smoky quartz, calcite, hematite, or siderite. Agates can be found in Brazil, Uraguay, China, India, Madagascar, Mexico, and the United States. Many agates are normally an unattractive grey color and are only feebly patterned. They assume their brightly colored appearance and striking structures only by being dyed. The extent to which the individual layera take on color varies according to porosity, water content, and crystallinity.
Banded agate: Layers parallel
to the outer surface In its wider sense chalcedony includes microcrystalline quartz (agate, true chalcedony, chrysoprase, dendritic agate, heliotrope, hornstone, jasper, carnelian, moss agate, onyx, sard); in a narrower sense only the grey-blue variety.
Composition: SiO2 This information was gathered from the Handbook of Rocks Minerals & Gemstones by Walter Schuman, 1993
|
||
|
|
||||